PageRank: Detecting Fake Accounts
In 2016, Jake Owen, an American country music singer, shared a video with 1.8 million Facebook fans. He was angry in that video and swore that someone had used his name to send messages to girls!! Jake Owen is not the only famous person whose profile has been forged. Attackers use the information and recent activities of celebrities on the Internet to create a fake account. They use these cloned profiles to attract thousands of followers. Thus create problems for celebrities and even their fans. This phenomenon is commonly known as Identity Cloning Attack, which is abbreviated to ICA in the literature.
Some researchers have divided the approaches for detecting fake accounts into two categories: (1) methods that are based on extracting features from user activities and using these features to extract fake accounts with some classifiers (2) modeling the online social network as a graph and then dividing it into two regions separating the real accounts from the fakes ones.
Non-automatic detection: In general, most studies in this approach are based on the similarity measures and social relationships of the users. First, a profile is entered into the system as the victim’s profile. In the second step, the similarity between the victim’s profile and each candidate profile was estimated based on the attributes and the relationship between mutual friends of the real user and suspicious users. Users with a stronger social relationship are known as real users. The profiles whose similarity to the victim’s profile exceeded a predefined threshold moved to the last step. Finally, A human agent or a friend recognizes cloned profiles. The need for a human agent in the last step causes these methods to be called non-automatic.
Automatic detection: In short, automatic detection is like a non-automatic detection except in the final stage. If the similarity coefficient is larger than a predefined threshold, Specific information such as location information (IP address) and real communication are used to identify cloned profiles from real profiles. Nonetheless, employing these methods requires access to the servers of social networks and users’ personal information, which is a shortcoming of them. Dr. Khasteh and his team proposed an automatic method (Figure 1The proposed method) to identify cloned profiles.
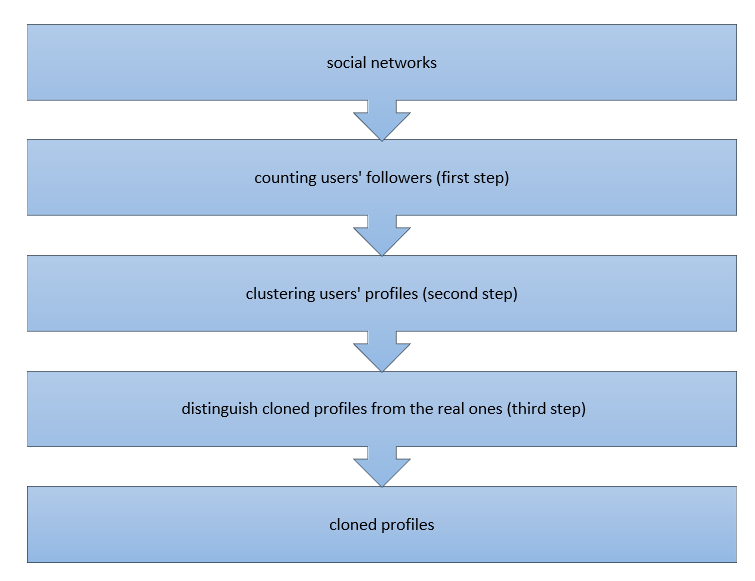
This method consists of three main steps:
In the first step, the number of network users’ followers are counted and stored as one of the user’s profiles attributes. This process is carried out using the MapReduce programming model. In the second step, the network users are clustered with k-means clustering algorithm based on their number of followers, and their profile attributes include gender, age, education, job, and location.
Subsequently, all the profiles which are in the victim’s profile cluster and have the same name are moved as the suspicious profile to the next step. The victim’s profile can be any profile that one wants to know that it has been cloned or not. As was mentioned earlier, attackers need to gain people’s trust to achieve their sinister goals. Although celebrities have a large number of followers, they follow a few users. Put simply, the number of followers to these profiles is larger than the number of followings. Therefore, in the third step, this property is used to detect real profiles.
In the third step, the PageRank algorithm is used to individuate cloned profiles from the real ones. In other words, the profile with the highest rank of the following is considered as the real profile.
“This method has advantages over previous methods: 1- Completely automatic and without the need for human agent intervention 2- Less running time 3- Using the clustering process instead of searching the whole social network 4- Reducing the required computation 5- Unlike previous methods, similarity measures, and a predefined threshold for it are not used to detect suspicious profiles, because it reduces system performance. 6- This method does not require any additional server information, including IP addresses, the sequence of users’ actions, or their click patterns. Instead, it has found the data available from the social networks sufficient,” Dr. Khasteh says.
Given the myriad features that social networks provide to users, many users regularly exchange and generate information. These networks contain large sets of data, so it is not easy to analyze and extract information from this type of data using conventional methods. Therefore, in this study, large data techniques have been used for analysis. The proposed method was tested on the data set extracted from Instagram and promising results. As a future study, the present method must be tested on more datasets from other online social networks. Furthermore, to increase the accuracy of this method, a combination of that with other automatic ICA detection methods such as Enhanced Clone Spotter can be provided. Also, this method and enhanced versions of it can be used for detecting other types of attacks possible in online social networks.





